Parkinson’s Disease and TCM: Alternative Treatments Worth Trying
Published | 7 min read
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease can be managed with modern medication and TCM treatments. Learn more about this progressive condition here.

Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that affects the brain, causing uncontrolled movement, stiffness in the limbs or the trunk, impaired balance, as well as mood and behavioural problems. There is no cure for the degenerative disorder, but there are medicines and treatments to help manage its symptoms and slow its progression.
Parkinson’s Disease: Signs and Symptoms

Parkinson’s disease symptoms vary from person to person, but there are four primary signs:
- Tremors or rhythmic shaking that often begins at the hands. A rhythmic back-and-forth motion involving the thumb and forefinger.
- Rigidity (muscle stiffness) or resistance to movement due to constant muscle contraction.
- Bradykinesia or a slowing down of spontaneous movement. This inability to automatically perform routine movements can frustrate people with Parkinson’s.
- Postural instability or impaired balance and loss of coordination can lead to more frequent falls.
Although symptoms develop slowly over the years — starting with hand tremors — people will eventually have trouble walking, talking, or completing other simple tasks as the disease worsens.
Aside from movement-related signs, it also includes non-motor symptoms such as depression, fear, anxiety, apathy, hallucinations, sleep disorders, and other cognitive impairments (dementia).
People with Parkinson’s can also have trouble swallowing and chewing, speech changes, urinary problems or constipation, smell dysfunction (anosmia) and blood pressure changes.
What Causes the Disease?
This neurodegenerative disorder predominately affects the dopamine-producing neurons in the brain called the substantia nigra. Dopamine is the chemical messenger responsible for transmitting signals to produce smooth, deliberate movements. Although many brain areas are affected, the most common symptoms happen when nerve cells (neurons) in the substantia nigra die or are impaired.
The nerve endings that produce norepinephrine are also compromised. Norepinephrine is the chemical messenger to the part of the nervous system that controls many automatic functions, including pulse and blood pressure. It may be why people with Parkinson’s experience fatigue and abnormalities in blood pressure regulation.
Although the exact cause of Parkinson’s is unknown, scientists believe the disease is triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Western Medicine Treatments
Parkinson’s disease treatments include medication or surgery to help manage and improve motor symptoms. If medications are ineffective, doctors can recommend deep brain stimulation. This surgical procedure involves inserting electrodes into part of the brain, which is connected to a device implanted in the chest. Together, they help painlessly stimulate the areas in the brain that control movement. This minimises tremors, slowness of movement, and rigidity.
TCM Therapies to Try
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), work stress, poor work-life balance, and unhealthy dietary and lifestyle habits may trigger Parkinson’s. This causes the formation and accumulation of pathogenic factors like Wind, Fire, Dampness, Phlegm, Blood Clots, and Stagnated Qi within the meridian channels, muscles, and sinews.
According to Real Medical Senior TCM Physician Brandon Yew, “As Parkinson’s disease is a systemic disease, it also affects the five major organs, the Liver, Heart, Spleen, Lungs, and Kidneys. Over time, as the disease progresses, Deficiencies of the qi, blood, yin (bodily fluids and cooling energy), and yang (warming energy) will arise, too.”
A licensed TCM physician will tailor herbal medication, acupuncture, and other therapies for every patient’s unique body constitution.
Herbal remedies

A study found that Tongtian Oral Liquid has neuroprotective and antioxidant effects in Parkinson’s disease-induced zebrafish. The formulation contains 11 herbal constituents. But it is Ligusticum chuan xiong (川芎), Gastrodia elata (tian ma, 天麻), Dahuruan Angelica root (bai zhi, 白芷), red peony root (chi shao, 赤芍), chrysanthemum (ju hua, 菊花), and liquorice root (gan cao, 甘草) that help reduce tremors and improve motion in the Parkinson’s disease-induced fish. It also allows growth to return to dopamine-producing neurons.
Lingzhi mushroom (also known as reishi) has been shown in a study to help improve symptoms of Parkinson’s disease when used in conjunction with Levodopa medication. The mushroom can also be used as a stand-alone therapy to help support the patient’s mental health.
Below are more TCM herbal formulations that may help:
- Di Tan Tang (涤痰汤): Dispels Wind, Dampness, phlegm, and Qi Stagnation
- Ban Xia Bai Zhu Tian Ma Tang (半夏白术天麻汤): Dispels Dampness, phlegm, and Wind; strengthens Spleen qi
- Zhen Gan Xi Feng Tang (镇肝熄风汤): Dispels Fire and Wind; regenerates blood and yin to nourish the Liver and Kidneys
- Tong Qiao Huo Xue Tang (通窍活血汤): Dissipates blood clots and unblocks the meridian channels for better qi and blood circulation
- Xiao Huo Luo Dan (小活络丹): Dispels Wind, Dampness, phlegm, and blood clots; unblocks the meridian channels for better qi and blood circulation
- Da Huo Luo Dan (大活络丹) (more potent than Xiao Huo Luo Dan): Dispels Wind, Dampness, phlegm, and blood clots; unblocks the meridian channels for better qi and blood circulation
- Bu Yang Huan Wu Tang (补阳还伍汤): Regenerates qi of the Heart, Spleen and Lungs to restore the meridian circulation; dispels Wind and blood clots
- Di Huang Yin Zi (当归饮子): Regenerates blood, yin and yang of the Heart, Liver and Kidneys; dispels Wind and phlegm
“As Parkinson’s disease is highly complex, patients are strongly advised against self-medicating with any TCM herbs or formulas lest they run the risk of aggravating their condition. They need medical help from a TCM professional,” cautions Physician Yew.
Acupressure
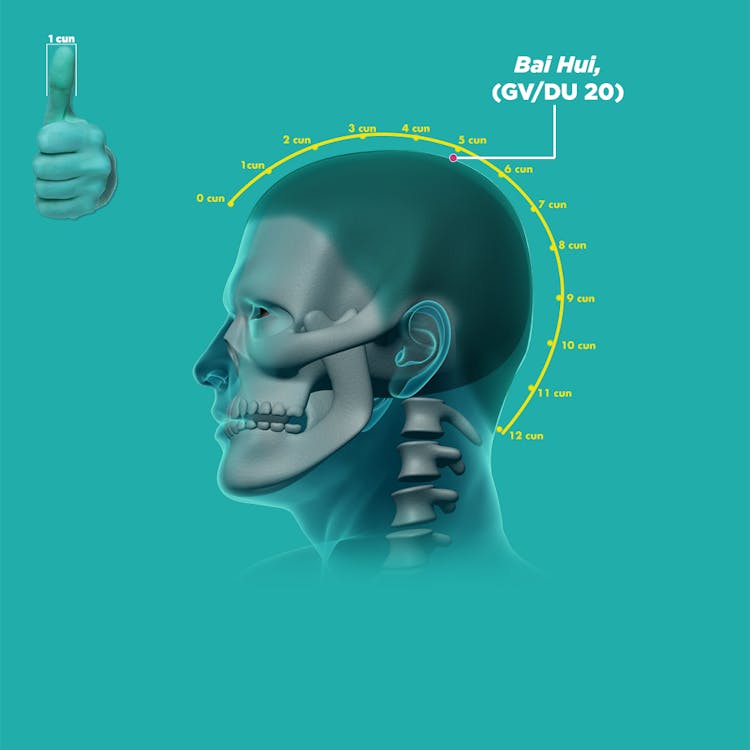
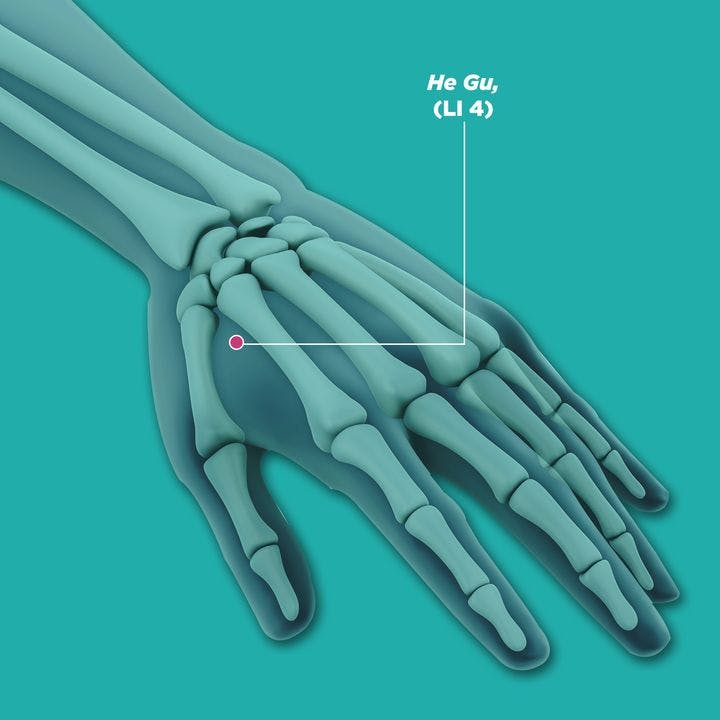
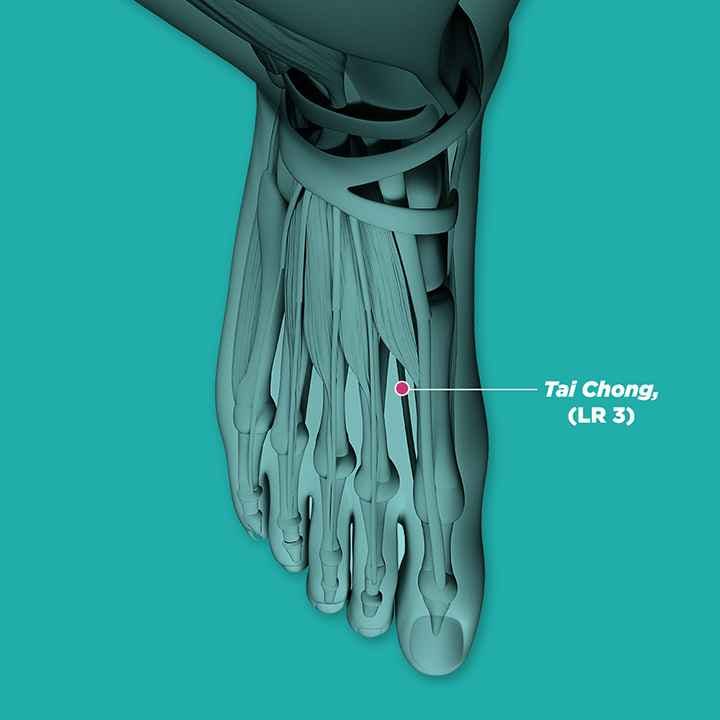
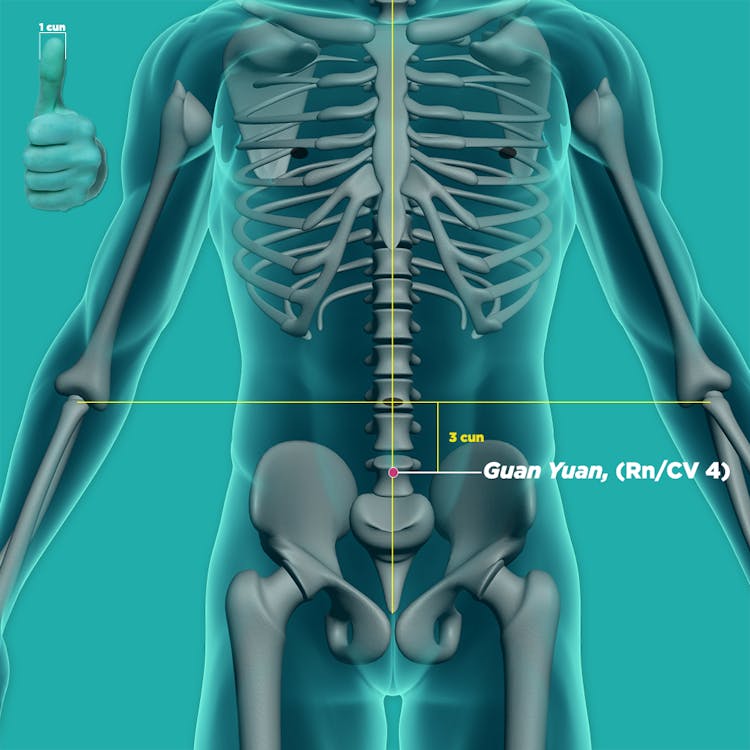
Using your fingers or a massage stick, place it at the specified acupoints and apply an appropriate amount of pressure. You should feel a tolerable sensation of soreness or tenderness. Massage the point, going clockwise and then counterclockwise, 20 times each. Repeat for at least three minutes per acupoint.
The acupoints that might help relieve mild symptoms of Parkinson’s are:
- Bai hui (DU20, 百会)
- Yin tang (EX-HN3, 印堂)
- Tai yang (EX-HN5, 太阳)
- Jing ming (BL1, 睛明)
- Tian tu (RN22, 天突)
- Shen men (HT7, 神门)
- Da ling (PC7, 大陵)
- He gu (LI4, 合谷)
- Zu san li (ST36, 足三里)
- Tai chong (LR3, 太冲)
- San yin jiao (SP6, 三阴交)
- Guan yuan (RN4, 关元)
- Qi hai (RN6, 气海)
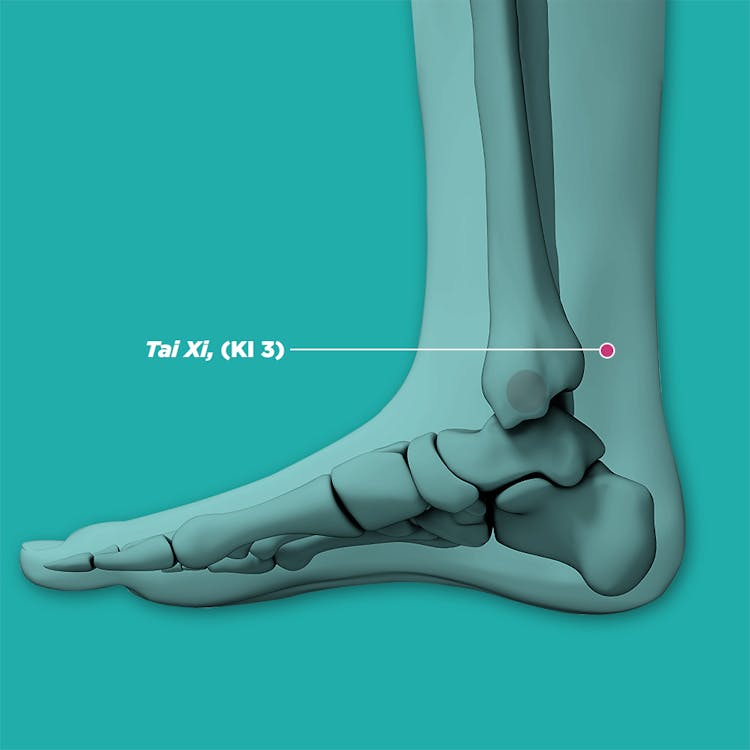
- Tai xi (KI3, 太溪)
Physician Yew warns that acupressure can only help manage mild symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. It’s still strongly recommended to seek professional TCM help, especially for those suffering from moderate to severe forms of the condition, in conjunction with a medical doctor.
Bookmark or share this article if you or anyone you know has Parkinson’s disease.
References
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 2020. Parkinson’s Disease: Hope Through Research. [Online] Available at: <https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/patient-caregiver-education/hope-through-research/parkinsons-disease-hope-through-research> [Accessed on 26 October 2022]
- Parkinson’s Foundation. What is Parkinson’s? [Online] Available at: <https://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/what-is-parkinsons> [Accessed on 26 October 2022]
- US National Library of Medicine. Last updated 2021. Effects of Lingzhi on Disease Progression in Patients With Untreated Early Parkinson’s Disease. [Online] Available at: < https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03594656> [Accessed on 26 October 2022]
- Journal of Medicinal Food. 2021. Self-Medication with Ganoderma lucidum(“Reishi”) to Combat Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms: A Single Case Study. [Online] Available at: <https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/jmf.2020.0137> [Accessed on 26 October 2022]
- Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2022. Neuroprotective effects of Tongtian oral liquid, a Traditional Chinese Medicine in the Parkinson’s disease-induced zebrafish model. [Online] Available at: <https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0753332222000944?via%3Dihub> [Accessed on 26 October 2022]
- National Institute On 2022. Parkinson’s Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments. [Online] Available at: <https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/parkinsons-disease> [Accessed on 26 October 2022]
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 2015. Parkinson’s Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Promise. [Online] Available at: <https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/patient-caregiver-education/hope-through-research/parkinsons-disease/parkinsons-disease-challenges-progress-a
Share this article on