What Are Ovarian Cysts and Should You Worry About Them?
Published | 8 min read
Ovarian cysts are masses in or on the ovaries, which are usually benign. However, they may cause problems at times. Here is all you need to know.

Did you know almost 20% of women develop an ovarian cyst or pelvic mass in their lifetime? Ovarian cysts are masses that grow on or inside the ovaries. There are as many as 30 different types of ovarian cysts. It might sound scary but most of them are functional cysts related to normal ovarian functions and not malignant in nature. However, at times, they can also be a sign of diseases such as
Ovarian cysts seen in women of childbearing age are usually benign and do not require surgical treatment. However, they can lead to complications such as cyst ruptures, pelvic pain, blood loss and ovarian torsion that require prompt treatment.
Causes and Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts

The exact cause of ovarian cysts is usually not known but certain risk factors may predispose you to them. These include undergoing infertility treatments, pregnancy, having a low thyroid hormone, cigarette smoking and tubal ligation surgery.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) recognises ovarian cysts as zheng jia (
The main organs involved are the Liver, Kidney and Spleen. Pathological factors responsible for ovarian cysts include:
Blo od Stasis due to Qi Stagnation
Internal emotional injury causes a depression of Liver qi, resulting in obstruction of the channels, and impeded flow in collaterals and blood circulation. The
Accumulation of phlegm-Dampness
Irregular eating and drinking result in depressed Spleen yang (active energy). The Spleen is unable to function effectively resulting in phlegm and Dampness. The imbalance in these factors leads to the obstruction of qi and blood.
Stagnation of Damp-Heat
During menstruation and after delivery, the uterine vessels are empty and deficient. As a result, there is insufficient healthy qi. Pathogenic Damp-Heat can invade in these conditions. It mingles with residual blood, stagnating in the uterus, and can result in an abdominal mass.
Most functional ovarian cysts are asymptomatic and may not be detected. Symptoms include one-sided pain or pressure in the lower abdomen. The pain may be sharp or dull and may be continuous or appear intermittently. If a cyst ruptures or undergoes torsion, a patient may suddenly experience severe pain with nausea and vomiting. Menstrual irregularities and abnormal vaginal bleeding could also be symptoms of ovarian cysts.
Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
If a doctor has detected you have an ovarian mass, they will first ask you to undergo tests to rule out pregnancy and ovarian malignancy. CA-125 is a biomarker that is raised in most cases of ovarian cancer. It is more accurate in diagnosing cancer when used along with ultrasonography of the pelvis, particularly in menopausal women with ovarian cysts.
Management of ovarian cysts depends on the type and size of the cyst, the patient’s age, menopausal status, and if there is any suspicion of malignancy.
Conservative treatment
Single ovarian cysts of less than 10cm in diameter are usually benign, regardless of the age of the patient. Hence, if you are asymptomatic, you’ll usually only be monitored with regular ultrasound examinations. Most functional ovarian cysts disappear spontaneously after several menstrual cycles.
Your doctor may prescribe
Surgical treatment
Large ovarian cysts, cysts that don’t go away, or those that cause more severe symptoms might need surgery. The surgery may entail removing only the cyst or an entire ovary, depending on each individual case.
Herbal remedies
TCM remedies can be used for functional cysts which are asymptomatic. Based on each case presentation, a TCM physician will be able to do a syndrome differentiation and formulate the right treatment.
Some of the
- Cang Fu Dao Tan Wan (苍附导痰丸): Used in cases of accumulation of phlegm-Dampness. The formula transforms phlegm and eliminates Dampness, promotes blood flow and disperses conglomerations.
Main ingredients: Poria (fu ling, 茯苓), prepared pinellia tuber with Alumen radix glyrrhigae calcaren (fa ban xia, 法半夏), dried tangerine peel (chen pi, 陈皮), liquorice root (gan cao, 甘草), Atractylodes Rhizome (cang zhu, 苍术), NutgrassGalingale Rhizome (xiang fu, 香附), Bile arisaema (dan nan xing, 胆南星), bitter orange (zhi ke, 枳壳), fresh ginger (sheng jiang, 生姜), and medicated leaven (shen qu, 神曲).
- Da Huang Mu Dan Tang (大黄牡丹汤): Used in cases of Stagnation of Damp-Heat. This formula clears Heat and eliminates Dampness, resolves
Stasis and disperses concretions.
Main ingredients: Rhubarb (da huang, 大黄), tree Peony bark (mu dan pi, 牡丹皮), peach seed (tao ren, 桃仁), Chinese waxground seed (dong gua ren,冬瓜子 ), and sodium sulfate (mang xiao, 芒硝).
Acupuncture
Just like herbal remedies, acupuncture is also recommended only in functional cysts that are not likely to rupture or undergo torsion. A TCM physician is able to differentiate the syndromes and prescribe the right acupoints for needling during a session.
The
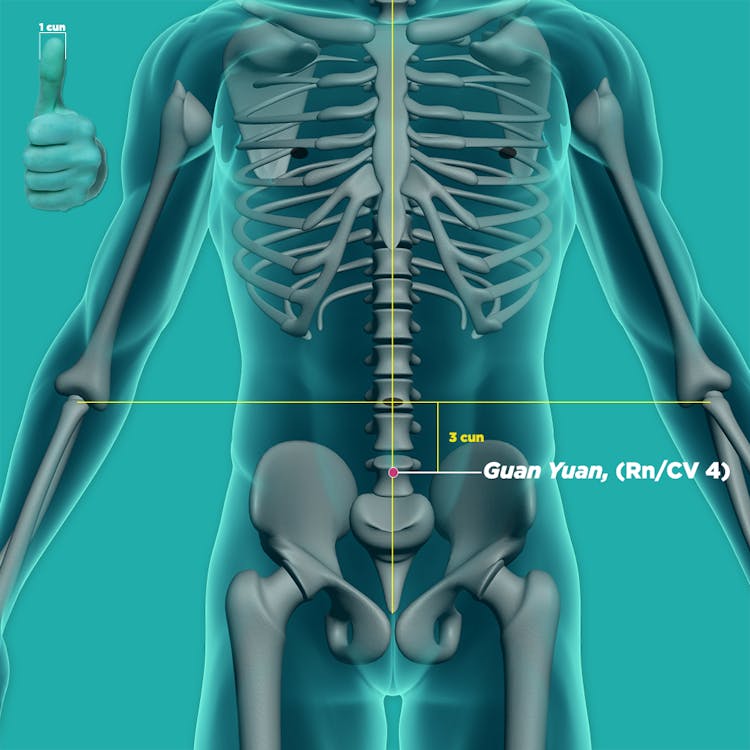
- For Blood Stasis due to Qi Stagnation: guan yuan (CV4, 关元), qi hai (CV6, 气海),
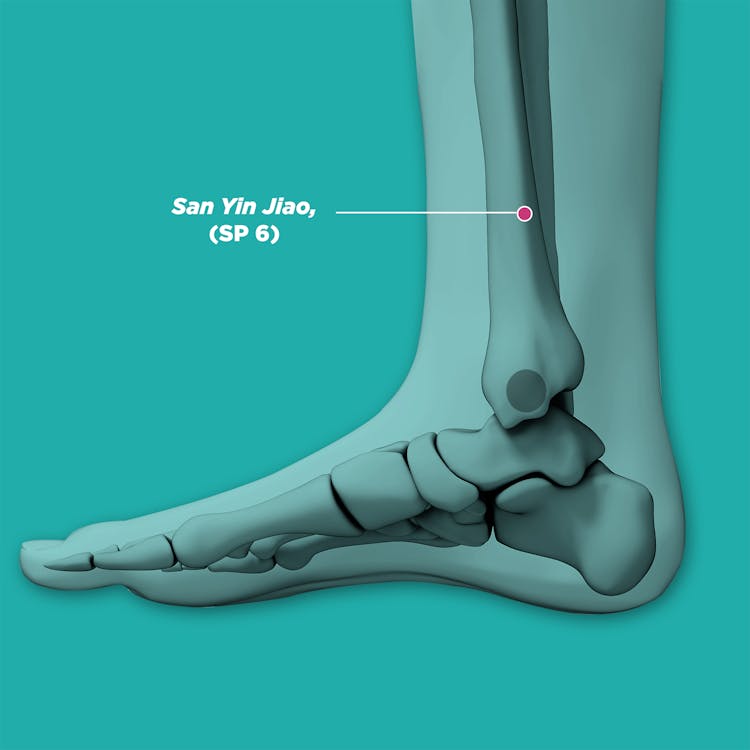
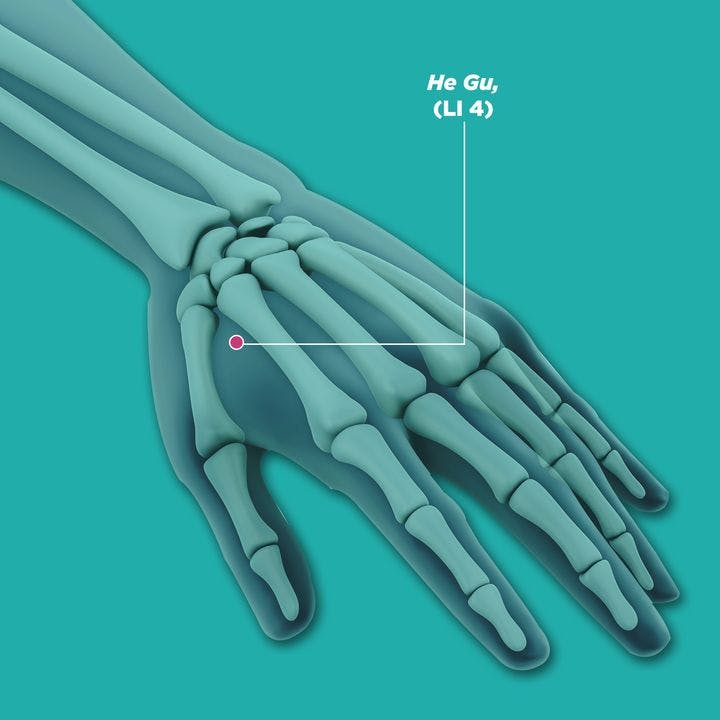
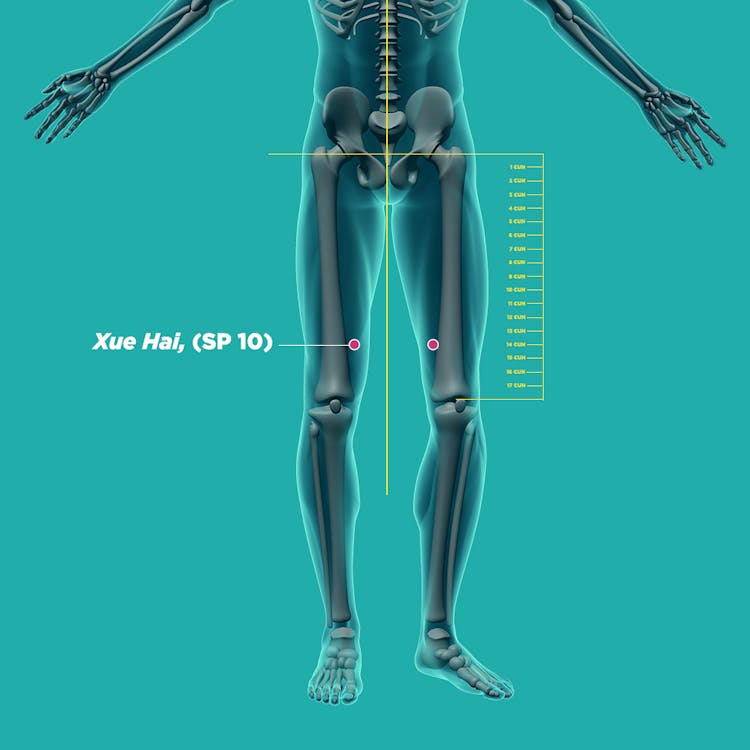
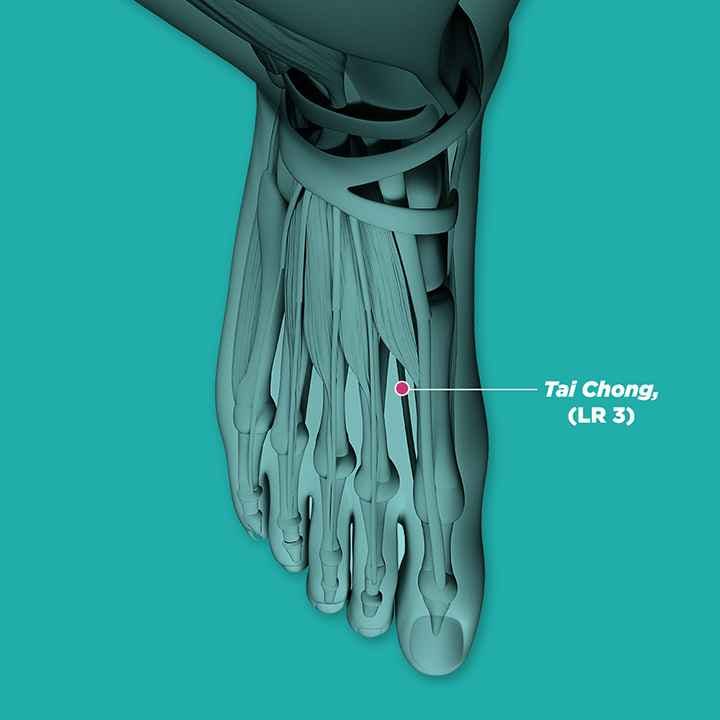
qi chong (ST30, 气沖), san yin jiao (SP6, 三阴交), he gu (LI4, 合谷), xue hai (SP10),ci liao (BL32 , 次髎),ge shu (BL17, 膈俞),shi men (CV5, 石门), and tai chong (LR3, 太冲)
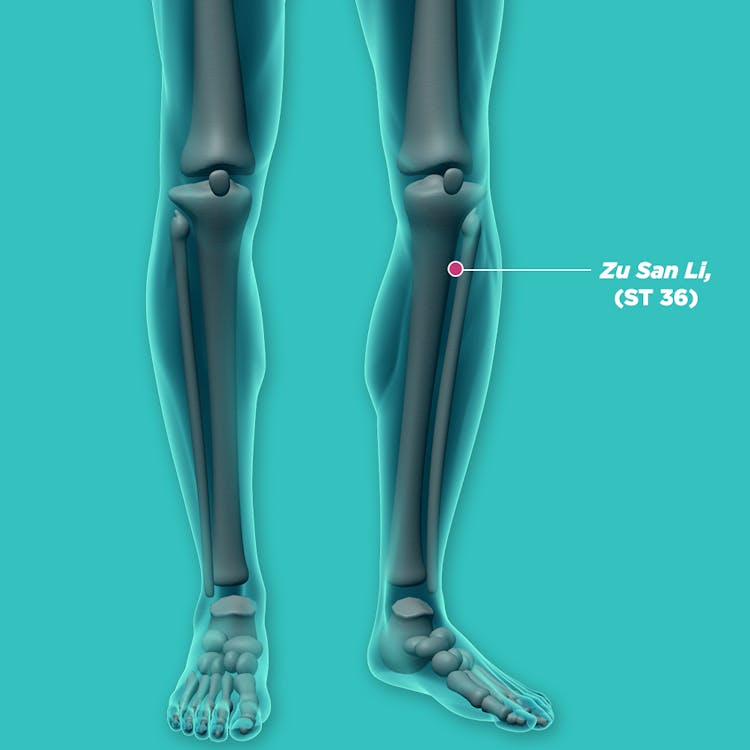
- Accumulation of Phlegm-Dampness: guan yuan (CV4, 关元), qi hai (CV5, 气海), feng long (ST40, 丰隆), zu san li (ST36, 足三里),
qu chi (LI11, 曲池), and di ji (SP8, 地机)
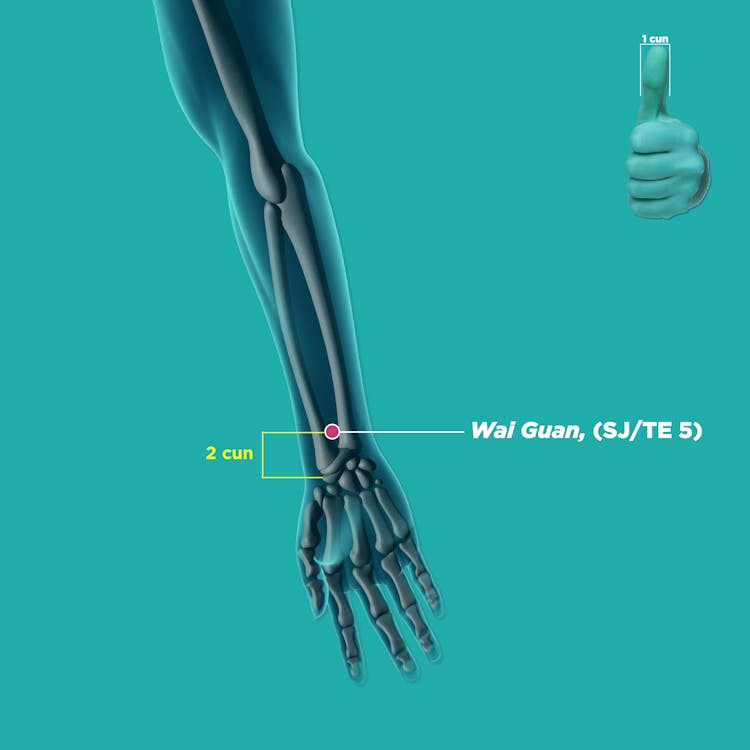
Stagnation of Damp-Heat: yin bai (SP1, 隐白) , tai chong (LR3, 太冲),shui dao (ST28, 水道), zhi gou, (SJ6, 支沟), and wai guan (SJ5, 外关)
Functional ovarian cysts are more common than you think. Thankfully, there are several treatment options in Western as well as a traditional medicine that can help to resolve them. Do approach your TCM physician for an in-depth syndrome differentiation so that you can be guided regarding the right treatment.
References
- StatPearls Publishing. Ovarian cyst. [online]Available at: Cancer Treatment Centers of America. What’s the difference? Carcinoma and sarcoma. [Accessed on 18 July 2022].
- Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica. Management of ovarian cysts [Accessed on 11 July 2022]
- Clinical and experimental obstetrics & gynecology. Current diagnosis and management of ovarian cysts. 2014. [Accessed on 18 July 2022]
Share this article on